2021-22 Science CH- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES (NOTEBOOK AND WORKBOOK EXERCISE)
CH- PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES(NOTEBOOK AND WORKBOOK EXERCISE)
NEW WORDS
1.galvanisation
2. rusting
3. antacid
4. anhydrous
5.reactivity
NEW TERMS
1.
anhydrous: a substance that is free from water.
2.
Reactivity: it is the tendency of a substance
to undergo a chemical reaction, either by itself or with other materials
Answer the following questions in one
word or a sentence.
a. What
is rust?
ANS. A reddish-brown layer of
iron oxide forms on iron articles which are exposed to air and moisture for a
period of time. This reddish-brown layer is known as rust. The process of
formation of rust is known as rusting.
b. State
the conditions necessary for rusting of iron.
ANS. 1.AIR. 2.MOISTURE
c. Give
two examples of antacids.
ANS. Magnesium hydroxide (milk
of magnesia), aluminium hydroxide, sodium carbonate and calcium carbonate are
common bases used as antacids.
d. Give
one example of a chemical change in which a change in colour is observed.
ANS. Cut fruits and vegetables
get blackened when they are left exposed to air.
The chemicals present in the
fruits and vegetables undergo a chemical change as they react with the oxygen
present in the air.
Answer the following questions in
brief.
a. Distinguish between physical and chemical changes.
ANS.
|
Physical change |
Chemical change |
|
Only physical
changes like odour, physical state, density, volume etc. changed and chemical
properties remain unchanged |
The chemical
composition and chemical properties undergo a change |
|
No new substance
is formed in a physical change. |
A new substance
is formed in a physical change. |
|
Very little or no
energy in the form of heat, light or sound is usually absorbed or given out
in a physical change |
A chemical change
is always accompanied by absorption or evolution of energy |
|
It is a temporary
change |
It is a permanent
change |
|
The original form
of substance can be regained by simple physical method |
Original
substance cannot be obtained by simple physical method |
|
Most of the
physical changes reversible. |
Most of the
chemical changes are irreversible. |
Define the following.
i. Chemical equations
ANS. Chemical changes are also called chemical reactions
and are represented in the form of an equation known as a chemical equation
ii. Reactants
ANS. The original substances that take part in a chemical
reaction and change into new substances are known as reactants
iii. Crystallisation
ANS. Large crystals of pure substances can be formed from
their solutions. The process of formation of crystals from their solution is
known as crystallisation.
Give reasons.
i. Boiling of water
is a physical change whereas the boiling of an egg is a chemical change.
ANS. Boiling
of water is a physical change as the water changes into water vapor and can be
reversed. But boiling of an egg is a chemical change because it cannot be reversed.
ii. Iron coated with
paint or grease does not rust.
ANS. Paint or
grease form a layer on the iron article and prevent direct contact with moist
air and iron material.
Answer the following questions in
detail.
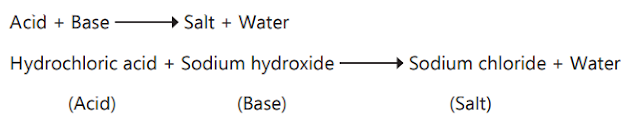
a. Explain the process of neutralisation with an example.
ANS. A reaction in which an acid and a base react to form
salt and water is called a neutralisation reaction.
b. What are physical and chemical properties?
ANS. A physical property is a characteristic of matter that
is not associated with a change in its chemical composition. Examples of
physical properties include physical state, size, shape, color, density,
hardness, electrical conductivity, melting and boiling points.
A chemical property
of a substance is a property that is observed during a reaction in which the
chemical composition or identity of the substance is changed. Combustibility,
reactivity, flammability are few examples of chemical properties.
c. Explain the function of antacids.
ANS. Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid for the
digestion of food. Sometimes the acids are produced in excess and they cause
acidity. Doctors give antacids to treat acidity. Antacids are weak bases which
neutralise the hydrochloric acid and the person gets relief from acidity.
Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia), aluminium
hydroxide, sodium carbonate and calcium carbonate are common bases used as
antacids.
Diagram based question.
a. What colour
change will you observe in the beaker shown in the diagram when an iron nail is
placed in it?
ANS.
The colour of the solution changes from blue to green.
b. What type of reaction takes place in the beaker when the
iron nail is placed in it?
ANS. Displacement reaction takes place.
Iron + Copper sulphate --------} Iron sulphate + Copper
HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
a. Do physical and chemical changes take place
simultaneously? Justify your answer with an example.
ANS. Yes, in
some cases the physical and the chemical changes can occur together.
One such example is the burning of candle. The wax present in the candle changes to liquid
state.
At the same time, the
constituents carbon and hydrogen present in wax react with oxygen of air to
form new substances.
b. What will you observe when a copper wire is placed in an
iron sulphate solution? Why?
ANS. When
copper wire is placed in iron sulphate solution there will be no change observed. This is because copper is less reactive than
iron, therefore, unable to displace it from its solution.
MIND MAP
LMR (LAST MINUTE REVISION NOTES)
LINK FOR WORKBOOK EXERCISE
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1eMdsnAW6dk6PEVScv9OEGQUlBNb6iMdp/view?usp=sharing


Comments
Post a Comment